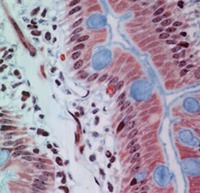
Above, the photograph shows the Parotid gland, which is a large salivary gland that consists of cells that are largely serous. It is divided into lobes by connective tissue septa. Clusters of gland cells are organized in Secretory acini. The cells are filled with granules. The saliva is collected in small ducts that leave the lobules and move out into the connective tissue between the lobes. Identify gland and duct cells in these photographs.

This view shows the granulated cytoplasm and the smallest ducts in the Parotid gland leaving a cluster of glandular cells.
The Submandibular Gland is a mixed salivary gland. Most of the glandular cells are serous. However some are mucus. In the following photograph, identify mucous cells, serous cells and duct cells.



In some of the acini, the serous cells form a cap (shaped like a half moon) over the centrally located mucous cells. This is called a SEROUS DEMILUNE. These photographs show the granules in the serous glandular cells as well as the mucous cells in the center of the demilune.

This shows a section of the submandibular gland stained with Masson's trichrome and Alcian yellow. The yellow stain detects the mucous cells. They are easy to distinguish.

This view shows a higher magnification of a serous demilune in the submandibular gland.
In the interlobar connective tissue, large EXCRETORY DUCTS can be seen. These are distinguished by their layers of nuclei and Goblet cells. The following photographs show views of this type of duct. Identify the Goblet cells.

Excretory ducts can also be found in the submandibular gland. They are distinguished by the the yellow staining Goblet cells. Higher magnification showing Goblet cells in the EXCRETORY DUCT of the Submandibular gland. What is the difference between intercalated ducts and striated ducts?

Classify the epithelium in the EXCRETORY DUCTS. Look at the lumenal cells for the proper “shape classification”.


The sublingual gland, seen below, has more mucous cells than serous cells. The above photograph shows a section of the sublingual gland. You can also see serous demilunes in this gland.


This view shows one of the ducts in the sublingual gland called the Striated duct. The nuclei have been pushed towards the lumen.
The surface specializations found at the base of these striated duct cells are lateral interdigitations, similar to those found in the kidney proximal tubule cells. They have sodium/potassium ATPases (pumps) that help with sodium and water conservation.
http://microanatomy.net/digestive/salivary_glands.htm
Gwen V. Childs, Ph.D., FAAA
Department of Neurobiology and Developmental Sciences
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
4301 W. Markham, Slot 510, Little Rock, AR 72205
For questions or concerns, send email to this address